问题来源
使用OpenCV 3.4.11在C++下跑YOLOv4的时候对
cv::dnn::Net::forward()函数的第一个参数产生了一些疑问,在此记录学习解惑的过程
代码来源:
- https://www.learnopencv.com/deep-learning-based-object-detection-using-yolov3-with-opencv-python-c/
- https://blog.csdn.net/guyuealian/article/details/84098461
网络模型训练自:https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet
使用dnn网络进行输入输出的代码:
1 | // 文件路径 |
在这里,函数getOutputsNames()的输出为网络中的三个输出层名称(函数代码在文末)。
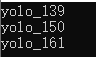
函数根据输出层名称得到如下的输出结果:
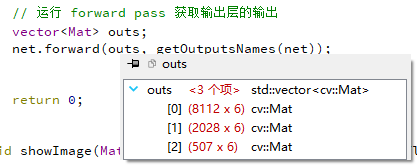
观察可得,的输出内容为一个数组,每个为6维度向量组(n行6列矩阵)
理解
官方文档:https://docs.opencv.org/3.4.11/
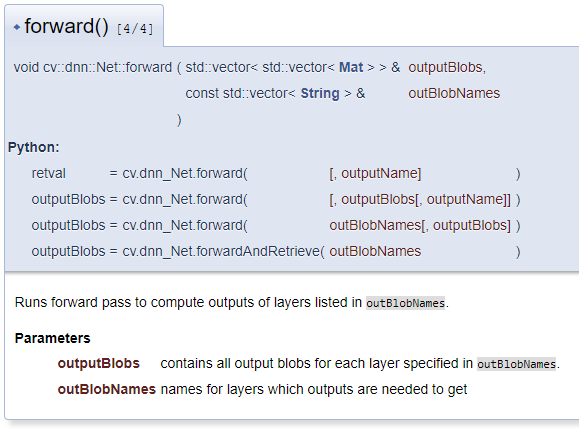
在上部分的调试信息中看到,outs数组的每一个元素都是一个6维向量,根据OpenCV官方文档的解释,该6维向量是每一个输出层的输出,形式为blob二进制对象,是根据不同的网络结构发生改变的数据结构。
在Sunita Nayak的文章中,找到了对YOLOv4网络结构下forward()函数输出的解释:

YOLOv4网络的输出为矩形框,每个矩形框由一个向量表示,所有矩形框组成一个向量组。每个向量的长度为类别数 + 5个参数,这五个参数的前四个分别是矩形框在图像上的位置center_x, center_y, width, height(均为比例,范围在0-1之间),第五个参数是该矩形框包含一个物体的置信度。
从向量的第五个参数开始,分别表示矩形框中物体对应每个类别的置信度。
在本文的例子中,自行训练的网络仅包含一个类,因此每个向量的长度为5+1=6。下面是一些数据例子:
| center_x | center_y | width | height | confidence of containing a object | confidence of class1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.503206133842 | 0.0607067160308 | 0.0554036833346 | 0.0370224379003 | 0.956498086452 | 0.947924435139 |
| 0.26918810606 | 0.0922166779637 | 0.0577514693141 | 0.034457128495 | 0.797747373581 | 0.791282773018 |
| 0.029834818095 | 0.00789603963494 | 0.0494357012212 | 0.0207939371467 | 0.000170804531081 | 0.0 |
处理forward()函数输出outs的详细代码及注释见文末。
附
getOutputsNames()函数代码1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20vector<String> getOutputsNames(Net &net)
{
vector<String> names;
if (names.empty())
{
// 获取输出层的索引号
vector<int> outLayers = net.getUnconnectedOutLayers();
// 获取网络中所有层的名称
vector<String> layersNames = net.getLayerNames();
// 将 cv::String 转为 std::string
names.resize(outLayers.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < outLayers.size(); i++)
{
names[i] = layersNames[outLayers[i] - 1];
}
}
return names;
}postprocess()函数
1 | void postprocess(Mat& frame, const vector<Mat>& outs) |